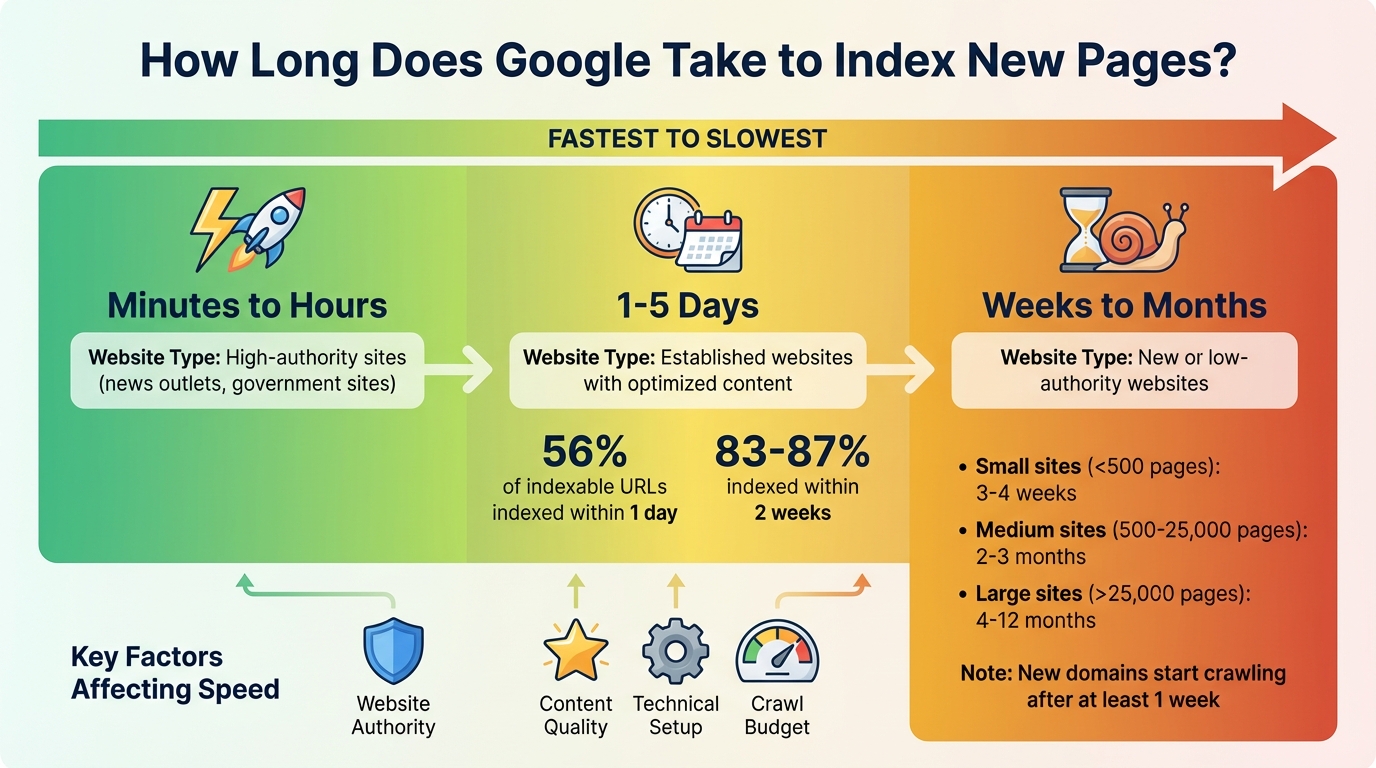
Google takes anywhere from a few hours to several weeks to index new pages. The exact time depends on factors like your website's authority, content quality, and technical setup. Here's a quick overview:
- Fast Indexing (Minutes to Hours): Common for high-authority sites like news outlets.
- Moderate Indexing (1–5 Days): Typical for established websites with optimized content.
- Slow Indexing (Weeks to Months): Happens with new or low-authority websites.
Key Factors Affecting Indexing Speed:
- Website Authority: Trusted sites get indexed faster.
- Content Quality: Original, valuable content aligns with Google's ranking criteria.
- Technical Setup: Issues like "noindex" tags or slow servers can delay indexing.
- Crawl Budget: Larger or poorly structured sites may experience slower indexing.
How to Check Indexing Status:
- Use
site:yourdomain.comin Google Search. - Use Google Search Console's URL Inspection Tool for detailed insights.
Ways to Speed Up Indexing:
- Submit an XML sitemap via Google Search Console.
- Build internal links to key pages.
- Fix technical issues like slow page speeds or crawl errors.
- Request indexing for specific URLs in Search Console.
If your page isn't indexed within expected timeframes (1–5 days for established sites, weeks for new ones), troubleshoot using Google Search Console to identify potential blockers. Consistently updating content and addressing technical issues can help improve your site's visibility.
Factors That Affect Google's Indexing Speed
Site-Level Factors
How quickly Google indexes your content often hinges on your website's reputation and technical setup. Websites with established authority - think major news outlets or government sites - can see their pages indexed in just minutes or hours because Google trusts their credibility. On the flip side, newer websites might face a waiting period that ranges from 4 days to 6 months as Google assesses their reliability.
Another key factor is your site's crawl budget - essentially, the number of pages Googlebot is willing to crawl. This budget is influenced by several elements, including your site's authority, size, traffic levels, and server performance. For instance, news websites that frequently update content tend to have a higher crawl demand. If your server responds quickly, Googlebot can crawl more pages; if it's slow, the crawl rate drops.
A solid linking strategy also plays a big role. Quality backlinks from trusted websites signal to Google that your content is worth indexing. Internally, a well-structured linking system, especially links from your homepage to key pages, helps Googlebot identify and prioritize important content.
While the reputation of your site sets the stage, the quality of individual pages and their technical configurations further impact how quickly they're indexed.
Page-Level and Technical Factors
Creating high-quality content is a must for faster indexing. Google prioritizes original, valuable content that aligns with its E-E-A-T principles: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Content that's low-quality, duplicated, or unhelpful may be ignored or take longer to index. However, as John Mueller, Google's Search Advocate, points out:
"A page can be of high quality and still not be indexed – it's not guaranteed".
Technical settings also play a critical role. Misconfigured robots.txt files or "noindex" tags can block Google from indexing your pages entirely. Additionally, fast-loading pages and mobile-friendly designs are essential, especially since Google uses mobile-first indexing. Pages that aren't optimized for mobile devices may experience slower indexing.
Even with strong site and page-level optimizations, technical issues can still cause delays in indexing.
Common Causes of Indexing Delays
Server-related problems, like slow response times, timeouts, or 5xx errors, can cause Googlebot to reduce its crawl rate - or even stop crawling altogether. Similarly, relying heavily on JavaScript for content can slow down indexing, as Google often needs to render such pages in a second pass.
Poor site architecture is another common culprit. Infinite URL structures, such as never-ending calendars or overly complex filtering systems, can overwhelm crawlers and cause them to miss key pages. Deeply nested pages - those buried several clicks away from the homepage - also make it harder for Googlebot to discover content. Additionally, using multiple URL parameters for filtering can create duplicate content issues, leading to delays while Google determines the canonical version.
Force Google to Index Your Pages in 2025 (Page indexing Secrets)
How to Check if Your Page is Indexed
Now that you've got a handle on what affects indexing speed, it's time to confirm whether your pages are actually indexed. Here's how you can do it.
Quick Checks with Google Search Operators
One of the fastest ways to see if Google has indexed your page is by using the site: search operator. Simply type site:yourdomain.com/specific-page-url into Google's search bar. If your page shows up in the results, it's indexed. If it doesn't, the page hasn't been indexed yet.
Want to check more broadly? Use site:yourdomain.com to see all indexed pages on your domain, or narrow it down to specific sections with site:example.com/folder/. You can even search for pages containing specific terms using site:example.com "keyword". According to Google, for websites with fewer than 500 pages, search operators are a quick and effective alternative to the Page Indexing report.
"Search for page URLs rather than text, because your page might be indexed by Google, but might not appear in the first page of results." – Google Search Console Help
Pro tip: Turn off SafeSearch to avoid missing results. Keep in mind, though, that search operators only tell you whether a page is indexed - they won't explain why it isn't.
Using Google Search Console
For a more detailed look, Google Search Console is your go-to tool. With the URL Inspection Tool, you can enter any URL to check its indexing status, see the last crawl date, and identify any technical issues preventing indexing. If a page isn't indexed, you can use the "Test Live URL" option to see whether Google can currently access it without errors.
The Page Indexing Report offers a broader view of your site's health by categorizing URLs as "Indexed" or "Not indexed" and providing reasons for exclusions. However, this report only includes a sample of up to 1,000 URLs, so if a page doesn't show up, double-check using the URL Inspection Tool. For newer sites, about 83% of pages get indexed within the first week, but smaller sites (fewer than 500 pages) may take 3 to 4 weeks for complete indexing.
| GSC Tool | Best Use Case | Details Provided | | --- | --- | --- | | URL Inspection Tool | Checking a single page | Indexing status, last crawl date, canonical URL, mobile usability | | Page Indexing Report | Site-wide health check | Total indexed vs. non-indexed pages, error types (404, noindex, etc.) | | Sitemaps Report | Discoverability for URLs | Submitted sitemap status, URLs discovered |
Next, we'll explore how automated tools can make monitoring your indexing progress even easier.
Monitoring Indexing Progress with IndexMachine
While Google Search Console provides the basics, IndexMachine takes it a step further by automating the entire process. This platform syncs with your Google Search Console account and makes tracking indexing progress a breeze. Instead of manually checking URLs or refreshing reports, IndexMachine offers visual progress tracking with charts that show how many pages are indexed over time.
It also sends daily reports summarizing your indexing status, flags 404 errors that need fixing, and provides detailed page insights. This means you can easily spot trends or issues without juggling multiple tools or spreadsheets. For those managing multiple domains, IndexMachine's centralized dashboard simplifies everything, so you can monitor all your sites in one place and address any indexing delays or problems quickly.
How to Speed Up Google's Indexing Process
If you want Google to index your pages faster, focus on improving both their discoverability and crawlability. Here's how you can make that happen.
Make Your Page Discoverable
Start by submitting an XML sitemap through Google Search Console. This acts like a roadmap, guiding Google to all your important URLs. It's especially helpful for new websites or those with a large number of pages.
Did you know that active blogs can lead to 434% more indexed pages? Regularly publishing new content encourages Google to crawl your site more often.
Internal links also play a crucial role. Linking from high-traffic pages creates a clear path for Googlebot to follow, improving your site's crawl priority. And don't underestimate the power of external backlinks. High-quality links from relevant, authoritative websites signal to Google that your site is worth discovering during its regular crawls.
Once your page is discoverable, the next step is to remove any technical obstacles that could slow things down.
Fix Crawl and Indexability Issues
Technical barriers can prevent Google from crawling or indexing your pages effectively. Here's what to check:
- Robots.txt file: Make sure it doesn't include a "Disallow: /" rule that blocks crawling.
- Meta tags: Remove
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">tags from pages you want indexed. - Canonical tags: Confirm they point to the correct URLs.
- 404 errors: Redirect these to live, relevant pages.
- Server issues: Use the Crawl Stats report in Search Console to identify problems like timeouts or 5xx errors.
Once these issues are resolved, you can take an extra step to prompt Google to index your page.
Request Indexing Through Google Search Console
For individual pages, the "Request Indexing" feature in Google Search Console is your go-to tool. Simply log in, paste the URL into the search bar, and if the page isn't indexed or has been updated, click "Request Indexing."
That said, keep in mind that this feature doesn't guarantee instant results. Google prioritizes high-quality content, and there's also a daily limit on how many URLs you can submit.
"Crawling and indexing are processes which can take some time and which rely on many factors. In general, we cannot make predictions or guarantees about when or if your URLs will be crawled or indexed." – Google
Avoid repeatedly requesting a recrawl for the same URL - it won't speed things up. For larger numbers of URLs or brand-new sites, submitting an XML sitemap through the Sitemaps report is usually a better option. After submitting, give Google at least a week before assuming there's a persistent issue.
When to Wait and When to Troubleshoot
Deciding whether to wait or troubleshoot indexing issues can save you time and effort. Around 56% of indexable URLs get indexed within a single day, and 83% to 87% of new pages are typically indexed within the first two weeks. However, these figures can vary widely depending on your site's authority and size.
Expected Indexing Timeframes
For established websites, indexing usually takes 1–5 days. If you're within this window, there's no need to take immediate action. For newer websites, the process often takes longer:
- Small sites (fewer than 500 pages): Full indexing may take 3 to 4 weeks.
- Medium sites (500 to 25,000 pages): Expect 2 to 3 months.
- Large sites (over 25,000 pages): This can range from 4 to 12 months.
For brand-new domains, Google typically starts crawling after at least a week.
If your page hasn't been indexed within these typical timeframes, it's a good idea to investigate. Start by using the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console (GSC) to identify any issues, such as noindex tags or robots.txt rules. Keep in mind that when you submit fixes through GSC, the validation process can take about two weeks, though delays are possible.
If the problem persists beyond these benchmarks, it's time to dig deeper and troubleshoot.
Troubleshooting Indexing Delays
When pages fail to index on schedule, here's how to approach the issue:
- Start with a site: search. This quick check can confirm if your page is indexed, bypassing the usual 2 to 4-day data lag in GSC reports.
- If your page still isn't indexed after a week, use the URL Inspection tool to review its Coverage status.
Pay attention to specific GSC messages:
- "Discovered – currently not indexed" indicates Google has found your URL but hasn't crawled it yet. This is often due to crawl budget limitations.
- "Crawled – currently not indexed" means Google has visited the page but decided not to index it, likely due to content quality or duplication issues.
It's also worth checking for broader industry updates. For instance, between November 21 and December 17, 2025, Google Search Console experienced a month-long reporting delay. During this period, data appeared stuck, even though indexing was functioning as usual. As Barry Schwartz, Executive Editor at Search Engine Roundtable, explained:
"The delay in the reporting has nothing to do with any issues with your site performance in Google Search. That was just a reporting delay and bug".
Conclusion
Earlier sections broke down the indexing process, but having a clear plan is crucial to make the most of every crawl opportunity. Established websites often see their pages indexed within days, while newer sites may take weeks to gain momentum.
Tips to Speed Up Indexing
Indexing happens in three phases: Discovery, Crawling, and Indexing. To improve your chances of faster indexing, it's important to optimize each stage. Start by ensuring your technical settings don't block search engine crawlers. Next, focus on creating unique, high-quality content that aligns with Google's E-E-A-T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). As John Mueller from Google puts it:
"A page can be of high quality and still not be indexed – it's not guaranteed".
For websites managing multiple domains or handling large volumes of pages, automation can simplify the process. Tools like IndexMachine integrate directly with the Google Search Console API, allowing you to submit pages automatically. With features like visual charts and daily reports, these tools help you monitor indexing progress and catch issues before they become bigger problems.
To sum it up, focus on streamlining the discovery process, fine-tuning your technical setup, and improving content quality to accelerate indexing.
Practical Steps for Website Owners
Ready to put these strategies into action? Start by checking your site's indexing status. Use the "site:yourdomain.com" search operator or review the Page Indexing report in Google Search Console. If you notice pages aren't being indexed within the expected timeframe, use the URL Inspection tool to pinpoint potential blockers. For time-sensitive pages, consider submitting them manually through Google Search Console - but remember, submitting multiple times won't speed things up.
Consistency is key. Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant, which encourages search engines to revisit your site. Keep your XML sitemap current, strengthen internal links, and address any technical issues flagged by Google Search Console promptly. By following these steps, you can minimize indexing delays and improve your site's visibility.
FAQs
What can I do to boost my website's authority and speed up indexing?
To boost your website's authority and speed up indexing, focus on creating reliable, well-researched content that naturally earns backlinks from trusted sources. Craft articles that address your audience's questions or problems, and promote them strategically through outreach or digital PR to secure links from respected industry websites.
On the technical side, make sure your site is in top shape. Use clear, keyword-focused title tags, well-structured URLs, and internal links to connect your new content with existing pages. A website that's fast, mobile-friendly, and secured with HTTPS not only builds trust but also helps reduce indexing delays. Regularly check for issues like broken links or crawl errors, and keep your XML sitemap updated to make it easier for Google to discover and index new pages.
Consistency is key - publishing valuable content on a regular basis increases the likelihood that search engines will crawl your site more frequently. Combine this with strong user engagement metrics, like low bounce rates and longer time spent on pages, to enhance your site's authority and improve indexing speed.
What should I check if my page isn't being indexed by Google?
If your page isn't showing up in Google's index, the first step is to check for technical issues that might be preventing it from being crawled or understood. Tools like Google Search Console are your best friend here. Use the URL Inspection tool to uncover problems like crawl errors, noindex tags, or blocked resources. The Page Indexing Report is another useful feature - it can reveal broader patterns across your site, such as server errors or URLs being blocked.
Here are some common culprits to investigate:
noindextags or robots.txt rules that might be unintentionally blocking Google from accessing the page.- Server errors (5xx) or slow response times, which could cause Googlebot to give up on crawling.
- Redirect loops or broken links that stop Google from reaching the page.
- Incorrect canonical tags that point Google to a different URL.
- JavaScript-rendered content that Google struggles to process.
After resolving the issue, head back to Search Console and re-submit the URL or sitemap. In many cases, this will prompt Google to index the page within just a few days.
How often should I update my website content to speed up indexing?
Regular updates to your website content signal to Google that your site is active and worth visiting more often. While there's no hard-and-fast rule for how frequently you should update, a solid approach is to review your content every three months. This helps you spot pages that might need a refresh. For pages featuring time-sensitive details - like news, pricing, or seasonal offers - aim for updates on a weekly or monthly basis. Meanwhile, evergreen content, which is designed to remain relevant over time, can be checked and updated annually to keep it accurate and useful.
Adding new content regularly, refining existing pages, or tweaking on-page SEO are all great ways to encourage Google to crawl your site more frequently. This can also potentially speed up the process of getting your pages indexed.